PROBLEM : we must create a stack using linked list with following specifications:
1. USING LINKED LIST
2. DYNAMIC IN SIZE
3. EACH STACK NODE CONTAINS AN ARRAY OF N(=5 in code) SIZE.
The code is shown below:
1. USING LINKED LIST
2. DYNAMIC IN SIZE
3. EACH STACK NODE CONTAINS AN ARRAY OF N(=5 in code) SIZE.
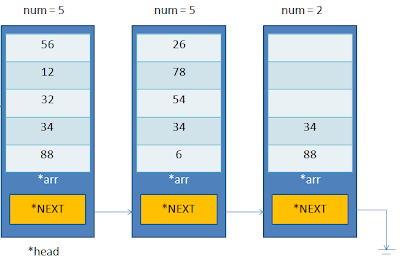 |
| SAMPLE DIAGRAM |
The code is shown below:
//TITLE DYNAMIC STACK
//AUTHOR VINAY CHOUDHARY
//DATE 26 OCT 2009
//This is a C program for DYNAMIC STACK
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<conio.h>
#define NUM 5
//pointer to array which is allocated memory at run-time. Can be //replaced by static
//array. Just comment out part where we are using malloc() for array //in push(). "num"
//tells how much data is present. "*next" is pointer to next stack
typedef struct blk
{
int *arr;
int num;
struct blk *next;
}stack;
//PUSH FUCTION : we pass head as pointer and data here.
//head is stored in backup for returning new value when
//stack is created for first time, else it contains old head value.
//In for loop we check if head exists and go to last stack,which has //next == null
//here we check if head(stack) exists or not or if array is
//full for current last stack. In both cases we create a new stack
//as temp. temp points to NULL, since it will be last stack
//and has no data at present so num = 0 for temp.
//now if stack doesnt exist then assign temp as head of stack since //we will add data to it. Also since this is new head store it in //backup for returning purpose,else if array has filled for current //last stack attach newly created temp stack to stack by storing its //address in next of curent stack and make head same as temp since //we add data to newly created stack(temp) using head(head=temp)
//add data
//and increment index. THIS INDEX CAN BE USED AS STACK POINTER
stack* push(stack *head,int data)
{
stack* backup,*temp;
for(backup = head;head && head->next != NULL;head = head->next);
if(head == NULL || head->num == NUM){
temp = (stack *)malloc(1*sizeof(stack));
temp->arr = (int*)malloc(NUM*sizeof(int));
temp->next = NULL;
temp->num = 0;
if(backup == NULL)
backup = head = temp;
else if(head->num == NUM)
head = head->next = temp;
}
head->arr[head->num] = data;
head->num = head->num + 1;
return backup;
}
//POP FUNCTION: we pass head as pointer and data as pointer here.
//temp will have first stack if there is only one stack else it //stores second last stack address
//in loop above we intialise temp = head and go to last stack //structure.
//decrement index. THIS INDEX CAN BE USED AS STACK POINTER
//and take data in pointer passed, which is collected in main.
//here we check if array of current last stack has become empty, if //so we need to delete it. But if there was only one stack (then //temp == head), make backup point to NULL and return it later, //since existing stack will //be removed.
//if there were more than one stacks, then delete last one. Since //temp has address of
//second last stack, use temp to make second last stack to point to //NULL. Hence stack pointed by temp is now the last stack. Free //memory of stack to be deleted.
stack* pop(stack *head,int *data)
{
stack* backup=NULL,*temp=NULL;
for(backup = head,temp = head;head->next != NULL;temp = head,head = head->next);
head->num = head->num - 1;
*data = head->arr[head->num];
if(head->num == 0)
{
if(temp == head)
backup = NULL;
temp->next=NULL;
free(head->arr);
free(head);
}
return backup;
}
void display(stack *head)
{
int i;
printf("\nCURRENT STACK: ");
if(!head)
printf("DOESN'T EXIST");
while(head)
{
for(i=0;i<head->num;i++)
printf("%d ",head->arr[i]);
head = head->next;
}
}
void main()
{
stack *head=NULL;
int data,run=1,cls=0;
char ch;
while(run)
{
display(head);
printf("\n\nWHAT TO DO ?");
printf("\n1. PUSH\n2. POP\n3. DISPLAY\n4. EXIT\nYOUR OPTION : ");
scanf(“%c”,&ch);
switch(ch)
{
case '1':{
printf("Enter number to push: ");
scanf(“%d”,&data);
head = push(head,data);
break;
}
case '2':{
if( (head) )
{
head = pop(head,&data);
printf("DATA POPPED: %d",data);
}
else
printf("CAN'T POP: NO DATA IN STACK");
break;
}
case '3':{
display(head);
break;
}
case '4':{
run = 0;
break;
}
default:{
system("cls");
printf("\nENTER VALID OPTION");
break;
}
}
}
printf("\n\n\);
}
No comments:
Post a Comment